This page last updated: 15 Dec 2022. Contact Shraddha Pai for the latest.
Our goal is to improve data-driven clinical decision-making, by understanding how the genome impacts phenotype at various levels of system organization. We take an interdisciplinary approach, combining molecular biology, genomics, computational and systems biology, to infer cell state in normal and diseased states.
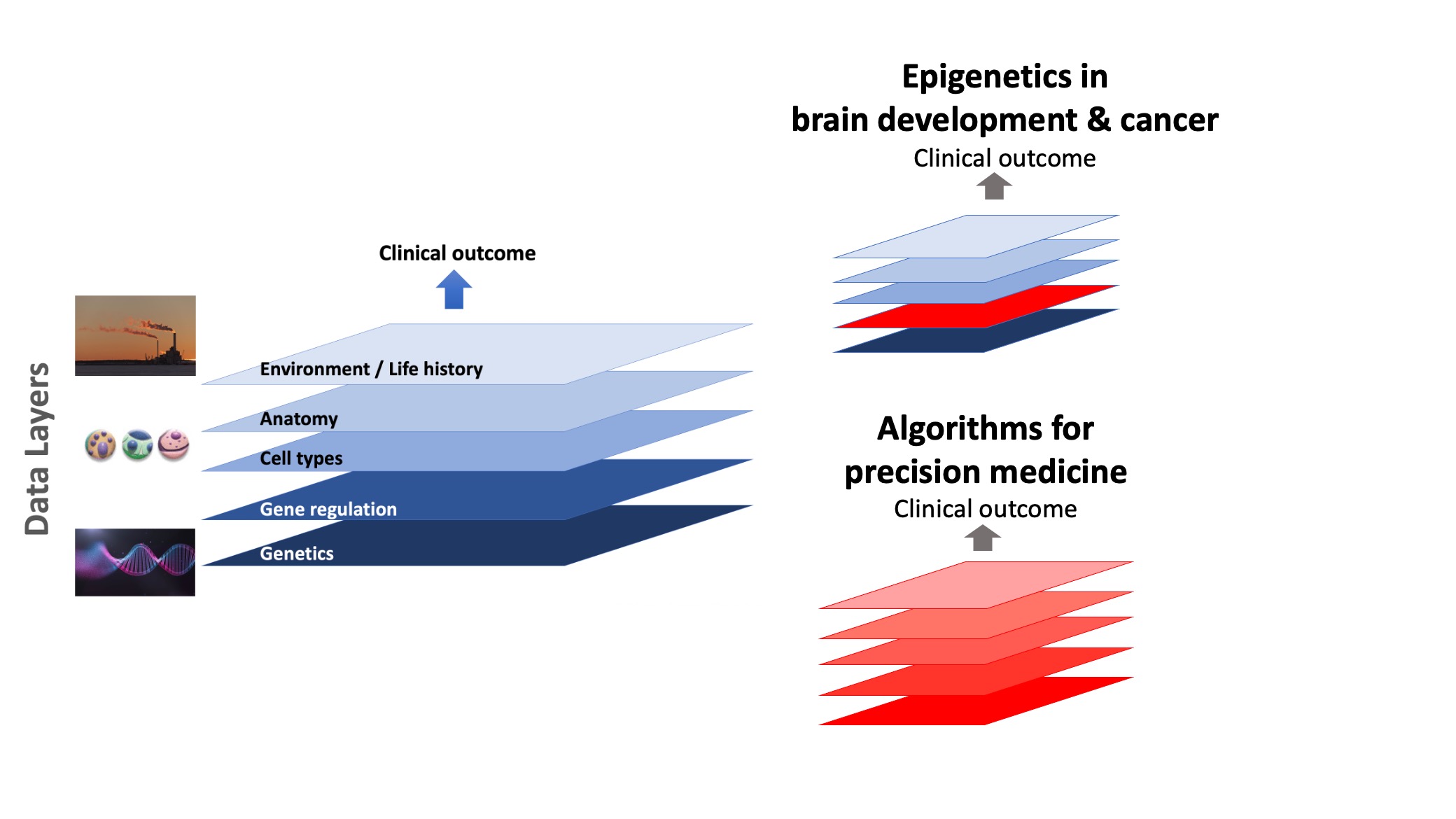
Epigenomic contribution to disease
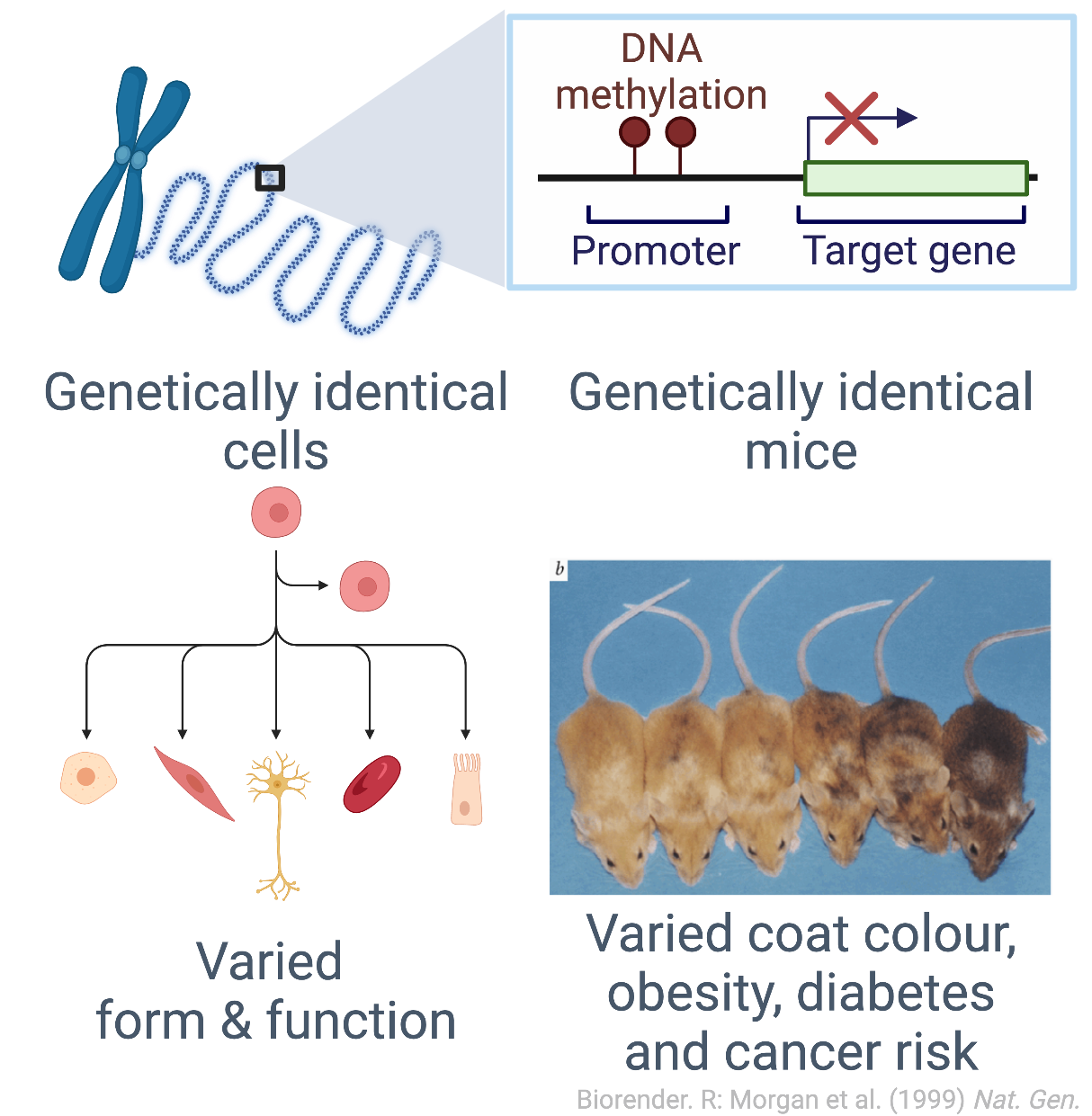 Epigenetic processes control gene expression programs, conferring cellular identity and function, and disease when dysregulated. Chromatin and DNA methylation state in the non-coding genome drives oncogenesis in some forms of pediatric brain cancer, and have diagnostic and prognostic value in other cancers. Epigenetics also provides a mechanism for interactions between genetics and the environment to alter genome regulation.
Epigenetic processes control gene expression programs, conferring cellular identity and function, and disease when dysregulated. Chromatin and DNA methylation state in the non-coding genome drives oncogenesis in some forms of pediatric brain cancer, and have diagnostic and prognostic value in other cancers. Epigenetics also provides a mechanism for interactions between genetics and the environment to alter genome regulation.
We analyze patient genomes and epigenomes to discover biomarkers of disase and treatment resistance. Our goal is to bring epigenetic diagnostics and therapies to the clinic.
Our neuron-specific epigenome-wide association study in major psychosis identified a novel epigenetic mechanism for dopamine dysregulation. We were also among the earliest to perform a genome-wide characterization of the brain-rich DNA modification 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine in human and mouse tissues.
Ongoing projects:
-
Do evolutionarily-recent gene regulatory networks make children vulnerable to brain cancer? single-cell transcriptomic analysis in human fetal hindbrain and Group 3 and 4 medulloblastoma; gene regulatory network inference
-
Does medulloblastoma arise due to epigenetic dysregulation? Single-cell DNA methylomics & transcriptomics in fetal hindbrain, and tumours. Collaboration with Gaiti Lab at Princess Margaret Cancer Centre and Taylor Lab at SickKids Toronto
 We’re looking Master’s or PhD candidate with programming and genomics expertise to lead bioinformatics. Contact Dr. Shraddha Pai with your CV if interested.
We’re looking Master’s or PhD candidate with programming and genomics expertise to lead bioinformatics. Contact Dr. Shraddha Pai with your CV if interested. -
Can the DNA methylome uncover a diagnostic biomarker for treatment-resistant glioblastoma? Uses EM-seq for DNA methylome profiling. Collaboration with Das Lab at St. Michael’s Hospital.
 We’re looking Master’s or PhD candidate with programming and genomics expertise to lead bioinformatics. Contact Dr. Shraddha Pai with your CV if interested.
We’re looking Master’s or PhD candidate with programming and genomics expertise to lead bioinformatics. Contact Dr. Shraddha Pai with your CV if interested. -
Can we link epigenomic alterations in disease to altered gene regulation, and nominate novel molecular targets? Algorithms for inferring gene regulatory networks from multi-omic data and epigenomic reference atlases
Algorithms for precision medicine
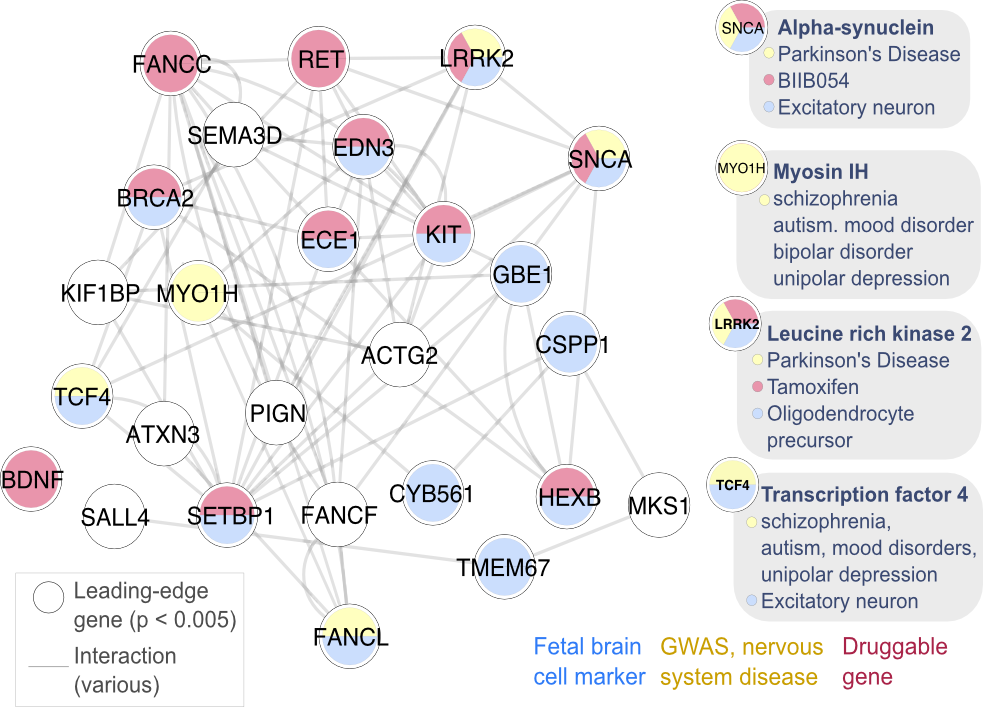 We develop computational methods to classify patients from multi-modal data and identify lead molecules for drug discovery. For this, we integrate diverse genomic databases of normal and disease state, including mutations, gene expression, epigenomics, molecular interactions, drug-gene interactions, single-cell genomics, and prior disease associations. We model molecular interactions using networks and a combination of data analysis, graph theoretic algorithms, interpretable machine learning and visualization.
We develop computational methods to classify patients from multi-modal data and identify lead molecules for drug discovery. For this, we integrate diverse genomic databases of normal and disease state, including mutations, gene expression, epigenomics, molecular interactions, drug-gene interactions, single-cell genomics, and prior disease associations. We model molecular interactions using networks and a combination of data analysis, graph theoretic algorithms, interpretable machine learning and visualization.
Ongoing projects:
-
Can we use molecular interaction networks to find novel cancer therapies? We are building an algorithm that integrates a large variety of normal and cancer genome profiles to prioritize lead molecules for therapies that will be effective and minimize side effects. Collaboration with Stein Lab (genomics) and Al-Awar group (Drug Discovery) and funded as a Prospect Grant by commercialization venture FACIT.
-
Can we predict clinical outcomes from multi-modal patient data?: We develop interpretable machine learning approaches that build in prior biological knowledge about tissue- and disease-specific genome regulation, and so provide mechanistic insight for effective hypothesis generation. Machine learning models using genomic data, need to be interpretable to minimize bias from small sample sizes and to drive rational drug design by providing mechanistic insight. We are interested in improving the ability to predict patient outcome by integrating multi-modal data, including clinical, genomic and imaging profiles.